The technology landscape in 2020s
They say 2020 is going to be a great start for another decade of disruption. Throughout the past 10 years, technology has changed the world inside and out: the birth of Ipad and Apple Watch, the arrival of so many “D”s (3D, 4D, 5D), the commercial introduction of Jet Pack or the mind-blowing event where Elon Musk brought his Tesla out of the orbit, thanks to multiple breakthrough technologies that genius figured out.
Then we had Pokémon Go unfolding the new way AR fought on the tech market, Sony’s PlayStation Move giving a break-through in motion control, and the wild debut of Sophia, the clever, cunning robot that reminds us of those old-school science fiction movies.
Those are only a shortlist. There were even more ground-breaking accomplishments scored in the last decade. It’s both astonishing and thrilling how humans could make many wonders in just a period of 10 years, which later intrigues a question: What will the technology landscape be in the next years? What more can humans do? What are the potential trends for the upcoming decade?
We are eager to make some predictions.
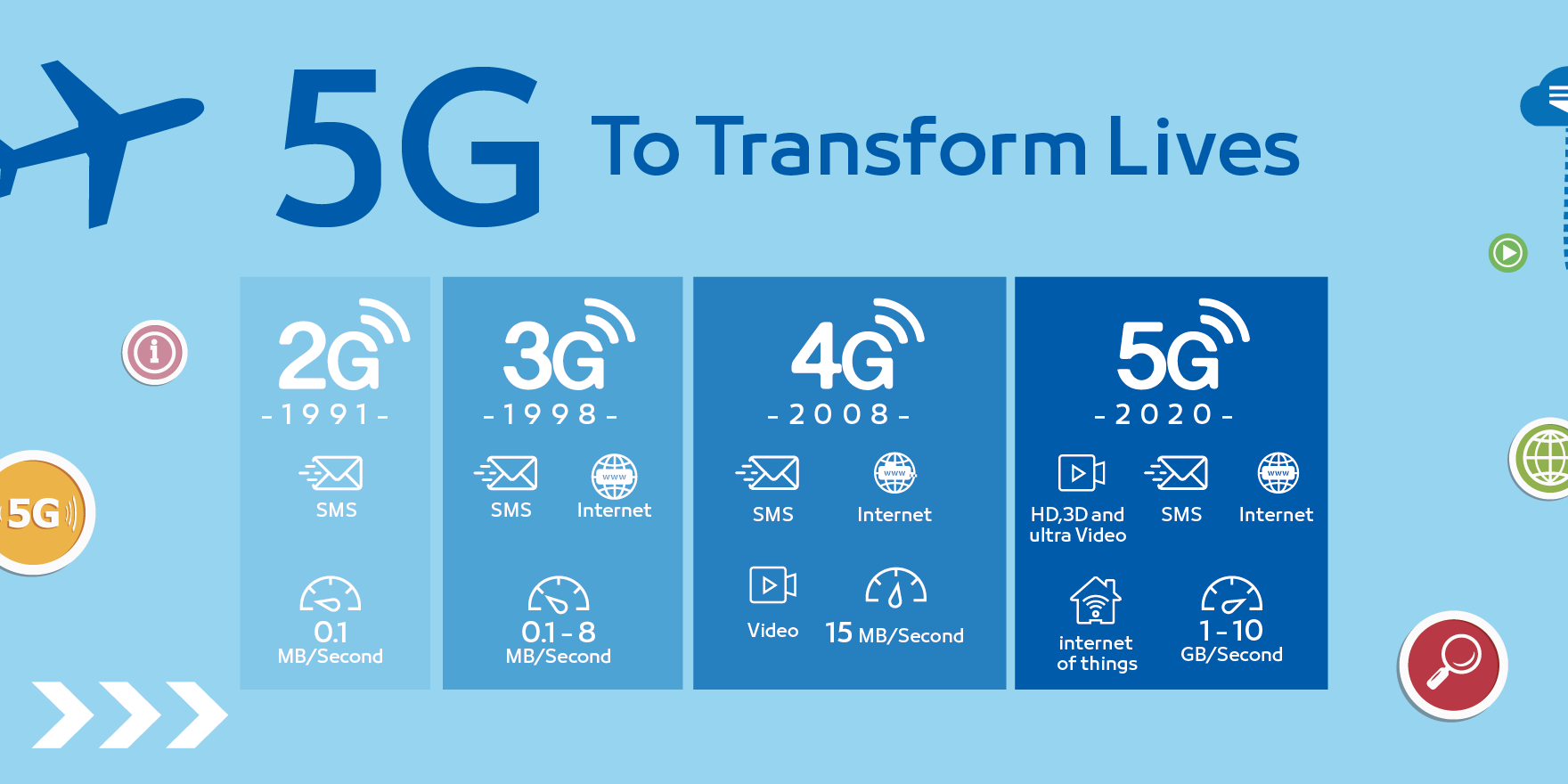
5G Network
5G is a new kind of network: a platform for innovations that will not only enhance today’s mobile broadband services, but also expand mobile networks to support a vast diversity of devices and services and connect new industries with improved performance, efficiency, and cost.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband: 5G will not only make smartphones better, but also usher in new immersive experiences, such as VR and AR, with faster, more uniform data rates, lower latency and cost-per-bit.
- Mission-Critical communications: 5G will enable new services that can transform industries with ultra-reliable/available, low latency links—such as remote control of critical infrastructure, vehicles, and medical procedures.
- Massive Internet of Things: 5G will seamlessly connect a massive number of embedded sensors in virtually everything through the ability to scale down in data rates, power and mobility to provide extremely lean and low-cost solutions.
- A defining capability of 5G is also the design for forwarding compatibility—the ability to flexibly support future services that are unknown today.
According to a forecast by Ericsson, by 2025, volumes of mobile data traffic are expected to increase by a factor of 4, and 45% of that traffic will be carried by 5G networks.
Furthermore, through a landmark 5G Economy study, we found that 5G’s full economic effect will be realized across the globe by 2035, supporting a wide range of industries and potentially producing up to $12 trillion worth of goods and services.
The study also revealed that the 5G value chain (OEMs, operators, content creators, app developers and consumers) could alone generate up to $3.5 trillion in overall aggregate revenue by 2035 and support up to 22 million jobs. That gives a decent shred of evidence for why 5G is going to be the next warhorse.
AI and Machine Learning as a “cure” for Cancer and HIV/AIDS
We are so tantalizingly close to a cure for two of the most vexing diseases of the past several decades: Cancer and HIV/AIDS. While we’ve been told numerous times over the years that a cure is near, we’ve only found successful ways to put certain types of cancer into remission or simply hold HIV/AIDS at bay for a while — not an outright cure for either. But the 2020s may finally see a legitimate treatment for both these diseases, potentially saving millions of lives in the process thanks to the creative applications of AI and Machine Learning.
With cancer, a radical new treatment called CAR-T is showing great promise, and other companies are claiming similar success. Throughout the process, AI and Machine Learning would make a change in CAR-T manufacturing, a time-consuming and resource-intensive endeavour that’s given many medical companíe headaches in the commercial roll-out.
One of the most potential practices we could expect is the future results of the 5-year AI alliance between Microsoft and Novartis. The contract was newly signed in 2019, promising a strategic decade for both companies and the human lives as well.
AI and Machine Learning, whether in the basic form of software or robotics, promise to elevate healthcare in the 2020s
The results of the research are impressive. By using this new AI-powered method, researchers saw a 33% reduction in the long‐term TDF maintenance dose (200 mg) compared to standard regimens (300 mg). This regimen keeps the HIV viral load below 40 copies/mL with no relapse during a 144‐week observation period.
With those successes, these two deadly diseases will likely be a thing of the past by decade’s end. And that’s not all — several other conditions may become much rarer, and those born in this decade will likely by and large make it into the 22nd century healthier than ageing generations before it.
The greater future of commercial drones with Blockchain and IoT
“Blockchain and IoT can solve the current and future problems of the drone delivery industry through secured ownership, access control, data logging, and peer-to-peer deliveries.”
Last year, the FAA predicted that 452,000 commercial drones would be in use by 2022, but now it expects the industry to hit that size around the beginning of next year. The FAA latest prediction is that the commercial drone market will triple over the next five years, hitting 835,000 aircraft by 2023.
With drones for commercial purposes quickly becoming a reality, the need for security, coordination and proper logging is a must for the future. Using Blockchain can help solve these problems immensely, and, combined with an IoT monitoring device that enables for multiple inputs from the drone, will allow any drone to become a more secure flying aircraft.
Blockchain combines many aspects of a good backend solution: decentralization, redundancy, fault tolerance, security, and scalability. Besides being architecturally sound, Blockchain acts as a verifier of all information that’s sent to it. Through unique cryptographic keys, this allows digital identities, signatures, and ownership to be easily verified and recorded in a ledger-like format. Sensor, analytical and trip data from drones can also be signed and recorded immutably on the blockchain, leaving a permanent trail of audibility behind.
On the other hand, as the IoT device is already configured to work directly with the blockchain, it simply needs sensor input from an outside source. In this case, the drone will supply all information to the IoT device, including flight telemetry, trip, geo-spatial and other ToF (Time of Flight) data.

A commercial drone developed by Amazon, utilising and innovating the best tech including Blockchain and IoT to enhance efficiency
Micro data centre maturity in Edge Computing
Micro data centres, which are serving as a core infrastructure for supporting edge computing solutions, have been well received by the marketplace. Across many industries (like fast food restaurant chains, for example,) these solutions dramatically simplify technology deployments. The ability to remotely monitor these systems also eliminates the need to place IT staff on site. Employees only need to plug in the system and push the start button for activation to occur.
However, when an issue occurs within these systems, administrators are still unsure of where the failing component is located among the larger network of devices. They are also unable to determine whether the issue is adversely impacting other local components.
In the future these types of issues will be resolved perfectly, providing better values to the value chains. Microdata centres will be viewed as a single integrated entity as opposed to a simple collection of parts. In addition, the advanced analytics that feeds the remote monitoring systems will indicate whether the microdata centre is unhealthy and provide the reasons why a specific component is causing an issue.
These types of capabilities result in a reduction in lifecycle management costs. Such a scenario is a clear example of how Microdata centre improvement can drive business value in unmanned enterprise spaces in the next decade.
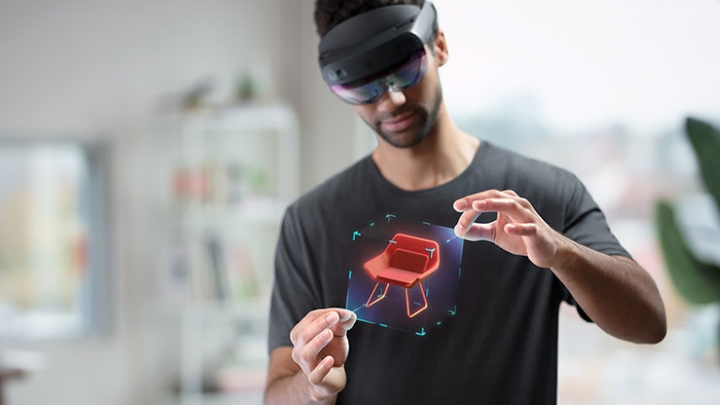
Mixed Reality
Mixed reality (MR) is an overlay of synthetic content on the real world that is anchored to and interacts with the real world—picture surgeons overlaying virtual ultrasound images on their patient while performing an operation, for example. The key characteristic of MR is that the synthetic content and the real-world content are able to react to each other in real-time.
Hardware associated with mixed reality includes Microsoft’s HoloLens, which associates with immersive and instinctual experiences to merge our real lives with digitality and make virtuality more realistic. This invention is set to be big in the MR industry – although Microsoft has dodged the AR/MR debate by introducing yet another term: “holographic computing”. Microsoft has just announced the upgraded version: HoloLens 2 emulator for developers so you can make applications for the new tech, still, the product is yet to be pronounced as “perfection”.
XaaS
We all saw this coming since the heydays of SaaS (Software as a Service). As cloud computing acted as a harbinger to PaaS (Platform as a Service), it was only a matter of time before Big Technology would move on to making Everything as a Service, where X stands for any function. Combined with the power of artificial intelligence and cloud computing, containerized functions will be made available to businesses or individuals, with intelligent, automated transactions to boost. The result of it is obvious: more productivity and more reliance on technology than the world has ever seen before.
If you are wishing to keep up with the forthcoming tech landscape and be the leader of the next decade, don’t hesitate to contact us. We are more than willing to be your partner for your future growth!
Contact us
- Phone: +84 24 3202 9222
- Hotline: +84326752886
- Email: [email protected]
- Official Website: https://savvycomsoftware.com/